MayaData Director is a remote SaaS management plane to provision and maintain OpenEBS persistent storage for your microservices running on Kubernetes.
Prerequisites:
- Kubernetes Cluster
- Each node should have at least one free unformatted disk attached to it. Prefer size larger than 10GB.
- Metallb loadbalancer configured on bare metal clusters to expose your services of type loadbalancer
- Flannel or Calico for CNI.
- Three Worker nodes size: 2VPUs x 8GB Memory (4VPU x 8GB recommended)
- One Master node size: 2VCPU x 8GB Memory (4VPU x 8GB recommended)
- CentOS 7.6/7.8 or Ubuntu 18.04 installed on the nodes with iSCSI client enabled
Configuration:
Enable iSCSI on the nodes
Check here for instructions.
yum install iscsi-initiator-utils -y
sudo systemctl enable --now iscsid
sudo systemctl status iscsid
Add cluster into the Kubera Director dashboard
Create kubera director login profile and login to the Kubera dashboard. Opt in for a basic plan for free access. This is sufficient to configure Kubera on couple of clusters.
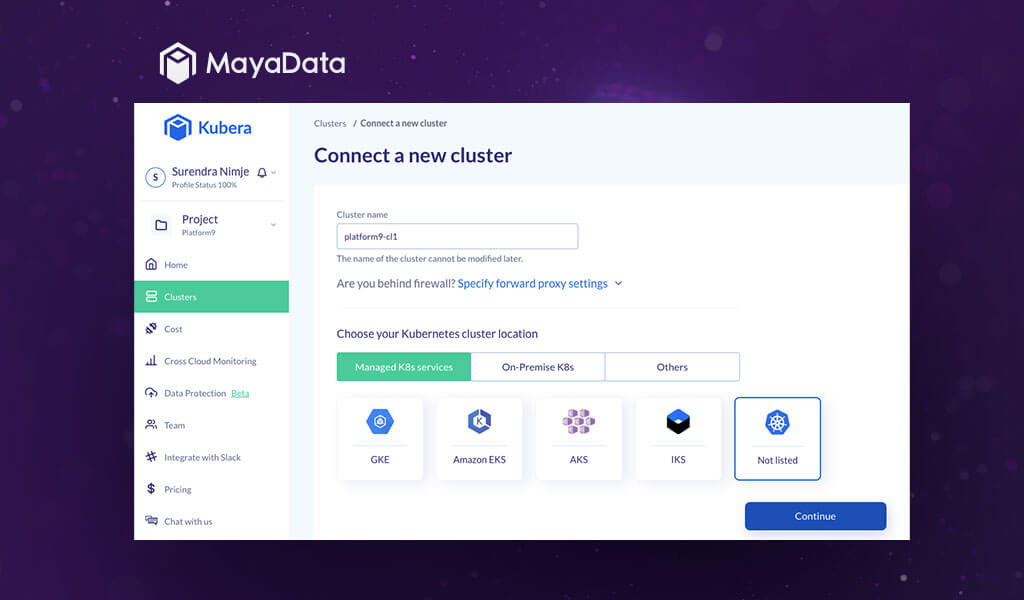
On the Dashboard create a project e.g. platform9 and add a cluster:
You’ll get the name of your cluster from the Platform9 SaaS management plane:
Now on the Kubera dashboard click ‘Connect a new cluster’ on the top right corner of the page. In the menu provide a name to your cluster, Select managed K8s services, select Not listed and click continue.
An ‘Activate cluster’ kubectl command will appear on your screen which should be simply copied as it is and run on your Platform9 kubernetes cluster.
How the above Manifest gets deployed on your platform9 cluster.
$ kubectl apply -f https://director.mayadata.io/v3/scripts/33CB85F3B5FC58858956:1609372800000:ZzmkeAxArnW8KkhsrBGSCZFrm2A.yaml
namespace/maya-system created
limitrange/maya-system-limit-range created
serviceaccount/maya-io created
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/maya-io created
secret/maya-credentials-a640881c created
job.batch/cluster-register created
daemonset.apps/maya-io-agent created
deployment.apps/status-agent created
configmap/publish-config created
deployment.apps/openebs-manager created
service/openebs-manager-service created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/openebses.dao.mayadata.io created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/adoptopenebses.dao.mayadata.io created
deployment.apps/openebs-upgrade created
serviceaccount/cstorpoolauto created
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/cstorpoolauto created
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/cstorpoolauto created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/cstorclusterconfigs.dao.mayadata.io created
statefulset.apps/cstorpoolauto created
daemonset.apps/pv-exporter created
configmap/cortex-agent-config created
deployment.apps/cortex-agent created
service/cortex-agent-service created
deployment.apps/upgrade-controller created
service/upgrade-controller-service created
In a few minutes activation is successful. After successful activation click Begin Installation on the ‘Install openEBS’ pop-up.
Select Advanced Installation
On the ‘Start installation’ screen click Next
Set resource limits suitable for a large applications
Select the Controler Nodes (for HA select all nodes in a small cluster)
Select Data nodes (Select all nodes with disks attached)
Setup filters to select disks for openEBS storage Pools
Confirm and deploy
Deployment progresses and finishes in few minutes
Verify deployment is running
Create new cStor Pool, select all nodes with disks attached and click create.
Validate Pool is ready
StorageClasses are created by default.
These Storage Classes will be visible in your platform9 SaaS management plane as well.
List down the storage classed via kubectl
$ kubectl get sc -o wide
NAME PROVISIONER RECLAIMPOLICY VOLUMEBINDINGMODE ALLOWVOLUMEEXPANSION AGE
openebs-device openebs.io/local Delete WaitForFirstConsumer false 12m
openebs-hostpath openebs.io/local Delete WaitForFirstConsumer false 12m
openebs-jiva-default openebs.io/provisioner-iscsi Delete Immediate false 12m
openebs-snapshot-promoter volumesnapshot.external-storage.k8s.io/snapshot-promoter Delete Immediate false 12m
Volume Provisioning
Now proceed to test the volume provisioning. Initially there are no volumes in the clusters.
$ kubectl get pv,pvc
No resources found in default namespace.
Create a test deployment and verify the PVC can be bound to the pod across the cluster.
$ kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/KoolKubernetes/csi/master/mayadata/kubera/test-deployment.yaml
persistentvolumeclaim/openebspodpvc created
deployment.apps/web-server created
The Pod, PV and PVC now can be seen default namespace
$ kubectl get pvc,pv,pods -o wide
NAME STATUS VOLUME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES STORAGECLASS AGE VOLUMEMODE
persistentvolumeclaim/openebspodpvc Bound pvc-06c9d68f-7557-417a-8b53-4a3c0962d205 5Gi RWO openebs-jiva-default 20s Filesystem
NAME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES RECLAIM POLICY STATUS CLAIM STORAGECLASS REASON AGE VOLUMEMODE
persistentvolume/pvc-06c9d68f-7557-417a-8b53-4a3c0962d205 5Gi RWO Delete Bound default/openebspodpvc openebs-jiva-default 19s Filesystem
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
pod/web-server-7658db5f8b-ksp2m 1/1 Running 0 20s 10.20.169.239 10.128.146.7 <none> <none>
Login to the NGINX which is running on 10.20.146.7 node and create a 1GB file on the PVC mounted inside the container.
$ kubectl exec -it pod/web-server-7658db5f8b-ksp2m -- /bin/bash
root@web-server-7658db5f8b-ksp2m:/#
root@web-server-7658db5f8b-ksp2m:/# cd /var/lib/www/html/
root@web-server-7658db5f8b-ksp2m:/var/lib/www/html# ls
lost+found
root@web-server-7658db5f8b-ksp2m:/var/lib/www/html# dd if=/dev/zero of=/var/lib/www/html/1GBfile bs=1M count=1024
1024+0 records in
1024+0 records out
1073741824 bytes (1.1 GB, 1.0 GiB) copied, 3.07405 s, 349 MB/s
root@web-server-7658db5f8b-ksp2m:/var/lib/www/html# ls -lrt
total 1048592
drwx------. 2 root root 16384 Apr 23 10:49 lost+found
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 1073741824 Apr 23 10:52 1GBfile
root@web-server-7658db5f8b-ksp2m:/var/lib/www/html#
Now cordon the node and delete the pod so that it can start the container on another node.
$ kubectl cordon 10.128.146.7
node/10.128.146.7 cordoned
$ kubectl get nodes
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
10.128.146.196 Ready worker 15d v1.18.10
10.128.146.56 Ready master 15d v1.18.10
10.128.146.7 Ready,SchedulingDisabled master 15d v1.18.10
10.128.146.99 Ready master 15d v1.18.10
$
$ kubectl delete pod/web-server-7658db5f8b-ksp2m
pod "web-server-7658db5f8b-ksp2m" deleted
$
$ kubectl get pv,pvc,pods -o wide
NAME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES RECLAIM POLICY STATUS CLAIM STORAGECLASS REASON AGE VOLUMEMODE
persistentvolume/pvc-06c9d68f-7557-417a-8b53-4a3c0962d205 5Gi RWO Delete Bound default/openebspodpvc openebs-jiva-default 4m33s Filesystem
NAME STATUS VOLUME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES STORAGECLASS AGE VOLUMEMODE
persistentvolumeclaim/openebspodpvc Bound pvc-06c9d68f-7557-417a-8b53-4a3c0962d205 5Gi RWO openebs-jiva-default 4m34s Filesystem
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
pod/web-server-7658db5f8b-8pthk 1/1 Running 0 28s 10.20.232.103 10.128.146.99 <none> <none>
Login to the pod and verify the file is present under the mount point.
$ kubectl exec -it pod/web-server-7658db5f8b-8pthk -- /bin/bash
root@web-server-7658db5f8b-8pthk:/# ls -lrt /var/lib/www/html
total 1048596
drwx------. 2 root root 16384 Apr 23 10:49 lost+found
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 1073741824 Apr 23 10:52 1GBfile
root@web-server-7658db5f8b-8pthk:/#
Enable Volume Analytics from the Dashboard to vizualize the statitics