This post has been updated by Kubernetes vs Docker Swarm.
—
In a previous blog we discussed why you would need a container orchestration tool and followed that up with a blog comparing Kubernetes vs Mesos. Continuing the series, in this blog post we’ll give an overview of and compare Kubernetes vs Docker Swarm.
Overview of Kubernetes
We gave an overview of Kubernetes in the blog comparing it with Mesos. For the sake of completeness, we’ll cover it again here.
According to the Kubernetes website – “Kubernetes is an open-source system for automating deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications.” Kubernetes was built by Google based on their experience running containers in production over the last decade. See below for a Kubernetes architecture diagram and the following explanation.

The major components in a Kubernetes cluster are:
- Pods – Kubernetes deploys and schedules containers in groups called pods. A pod will typically include 1 to 5 containers that collaborate to provide a service.
- Flat Networking Space – The default network model in Kubernetes is flat and permits all pods to talk to each other. Containers in the same pod share an IP and can communicate using ports on the localhost address.
- Labels – Labels are key-value pairs attached to objects and can be used to search and update multiple objects as a single set.
- Services – Services are endpoints that can be addressed by name and can be connected to pods using label selectors. The service will automatically round-robin requests between the pods. Kubernetes will set up a DNS server for the cluster that watches for new services and allows them to be addressed by name.
- Replication Controllers – Replication controllers are the way to instantiate pods in Kubernetes. They control and monitor the number of running pods for a service, improving fault tolerance.
Overview of Docker Swarm
According to the Swarm website, Docker Swarm provides native clustering capabilities to turn a group of Docker engines into a single, virtual Docker Engine. Swarm uses the standard Docker API, so normal docker run commands can be used to launch containers and Swarm will take care of selecting an appropriate host to run the container on. Other tools that use the Docker API, e.g. Docker Compose, can use Swarm without any changes.
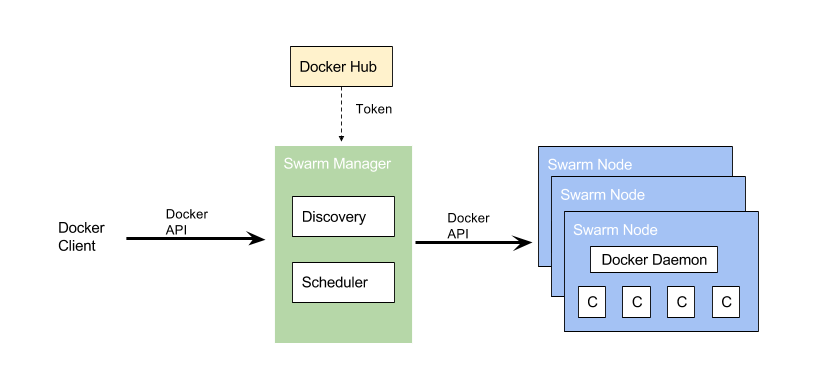
Each host in a Swarm cluster runs a Swarm agent and one host runs a Swarm manager. The manager will orchestrate and schedule containers on the hosts. Similar to other container orchestration tools, a Discovery service will find and add new hosts to the cluster. Third-party tools like Consul, ZooKeeper, etcd are required to ensure high availability and failover to a secondary Swarm manager.
The table below gives a detailed comparison of Swarm features with those of Kubernetes. For more detailed coverage of the container ecosystem, please download our Making Sense of the Container Ecosystem eBook.
Compare Kubernetes vs Docker Swarm
[table id=12 /]
In a follow up blog, we’ll answer why we chose to offer a Managed Kubernetes solution and explain the features and roadmap. For more details on the containers ecosystem, you can also download our Making Sense of the Container Ecosystem eBook.





