Create VMs
With the recent updates to version 5.4, we have implemented the following new features:
- A brand-new wizard to create VMs without the need to use YAML files
- We have added actions to start/stop the instance
- New details provided for the instances
- New options that list VM ownership
- Easily create and attach additional disk(s)
- The ability to create both Virtual Machines and VM Instances
Virtual Machines
Once you've enabled KubeVirt in your Kubernetes cluster via the PMK console cluster creation wizard, let's begin creating your first VM. We begin by navigating to the Virtual Machines section in the console.
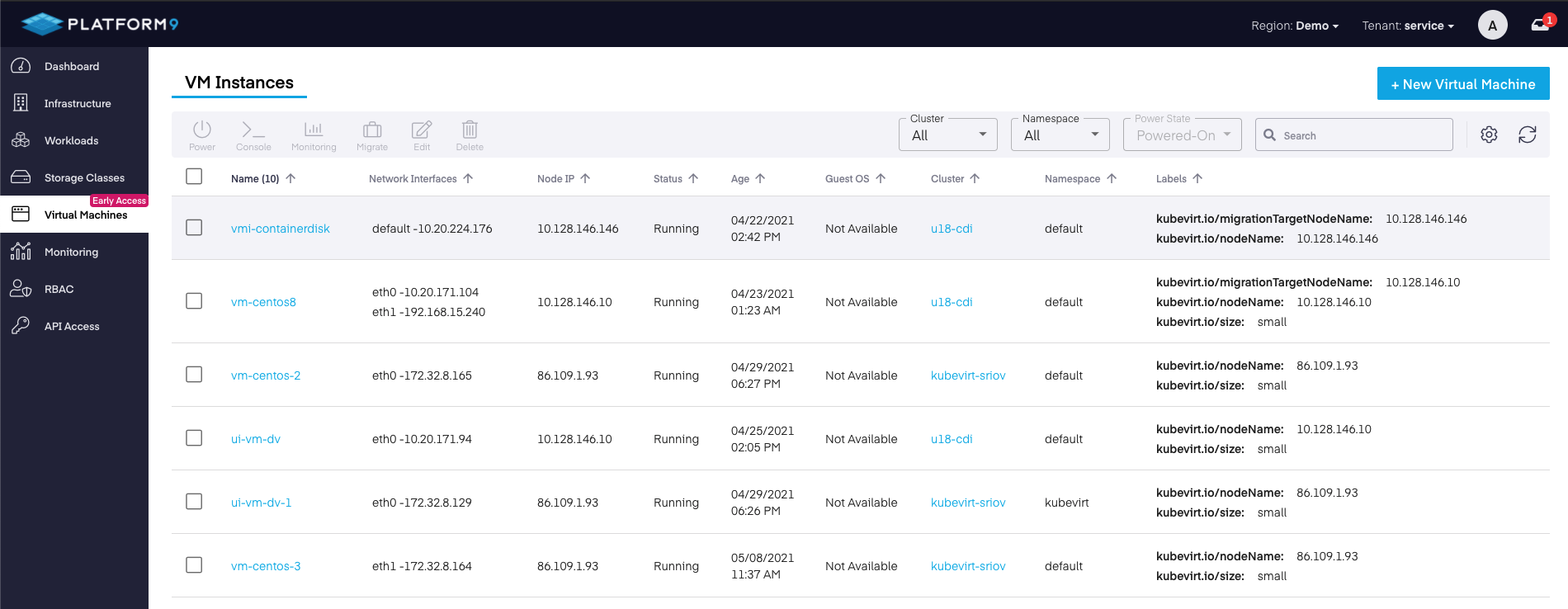
Next, click the
Configure VM
In the next step, we have two options; we can create the VM using a YAML file, or use the new Create a New VM Instance wizard.
- YAML file - Users can now use a YAML file to define the predetermined VM configuration settings included in the file. This makes for more reliable replication, better readability and increased reliability.
- Using the VM Instance wizard - With this option, you have the flexibility to input all the info specific to your needs using our UI.
Create VM using YAML File
After clicking on the
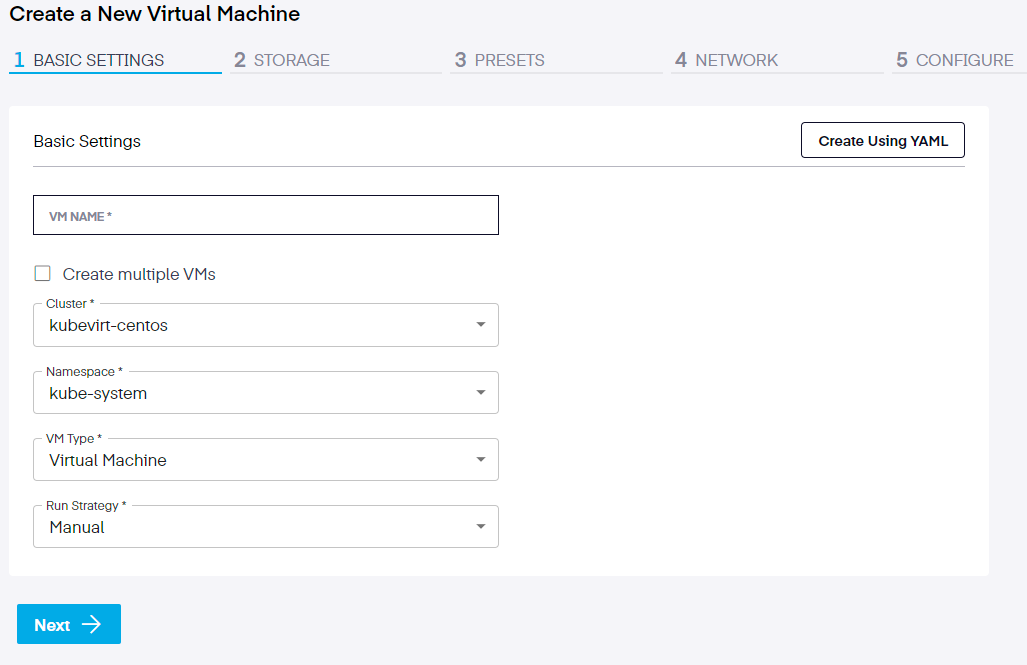
Next, click on the
Be sure to set the "VM Type" field to the correct value (i.e. VirtualMachine), based on the resource type specified in your YAML.
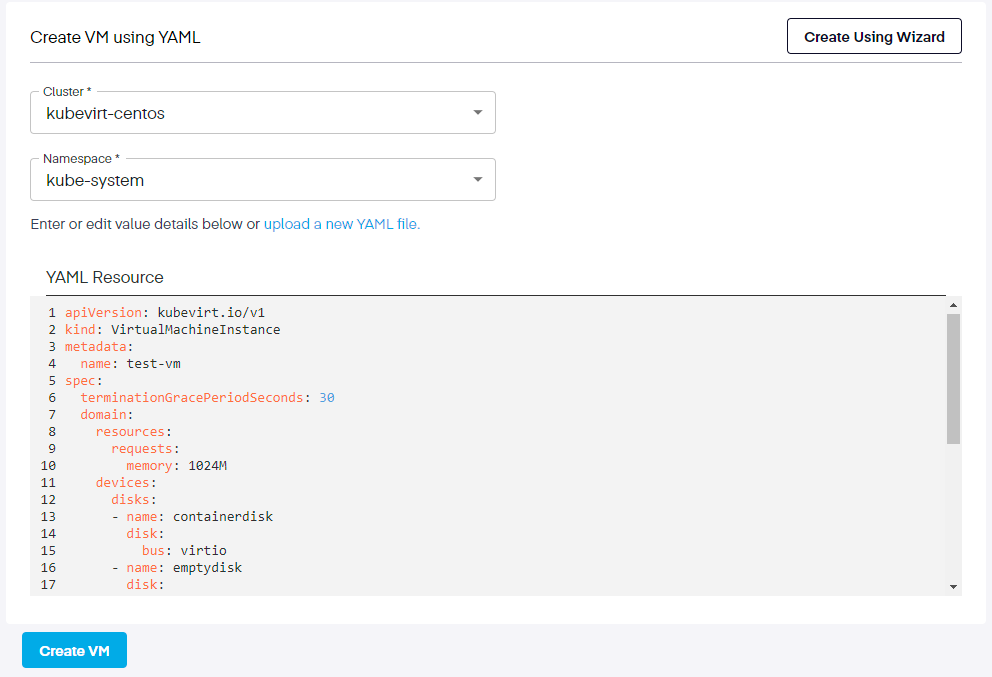
Below is a copy of the default YAML file we used. This can be utilized for testing in this environment. This example uses a fedora cloud image with cloud-init. To understand the details and more advanced options, refer to this section of the official KubeVirt User Guide. Add this sample Fedora VirtualMachine YAML into the VM creation wizard box.
apiVersionkubevirt.io/v1kindVirtualMachineInstancemetadata nametest-vmspec terminationGracePeriodSeconds30 domain resources requests memory1024M devices disksnamecontainerdisk disk busvirtionameemptydisk disk busvirtiodisk busvirtio namecloudinitdisk volumesnamecontainerdisk containerDisk imagekubevirt/fedora-cloud-container-disk-demolatestnameemptydisk emptyDisk capacity"2Gi"namecloudinitdisk cloudInitNoCloud userData- #cloud-config passwordfedora chpasswd expireFalse Your YAML file must be syntactically correct, or it will throw an error message stating: Provided YAML code is invalid.
Finally, click on the
Create a New VM Instance Wizard
The new method clients can use is the new Create a New VM Instance wizard.
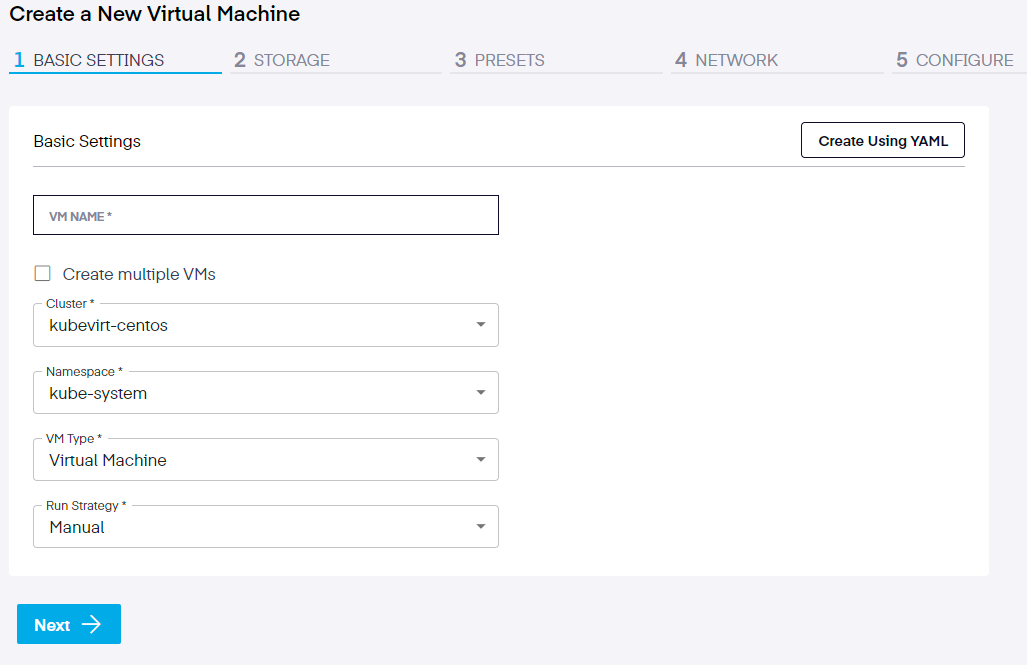
Step 1. Basic Settings
We begin by naming our VM. In this instance. Next, choose whether you will be creating a single or multiple VMs. If multiple, click the Create multiple VMs check box. Next, select the cluster and namespace the instance will be connected to, as well as the Run Strategy. There are four run strategies to choose from:
- Always - In this state, an instance will always exist. If it crashes, a new one will be created.
- RerunOnFailure - Here, an instance will be respawned if the former instance fails out in an error state. It will not be re-created unless it was shut down from inside the guest.
- Manual - The existence of an instance is limited exclusively to a start/stop/restart value in the VM subresource endpoint
- Halted - No instance will exist. If a guest is already running, it will be stopped.
For this tutorial, we have chosen Manual.
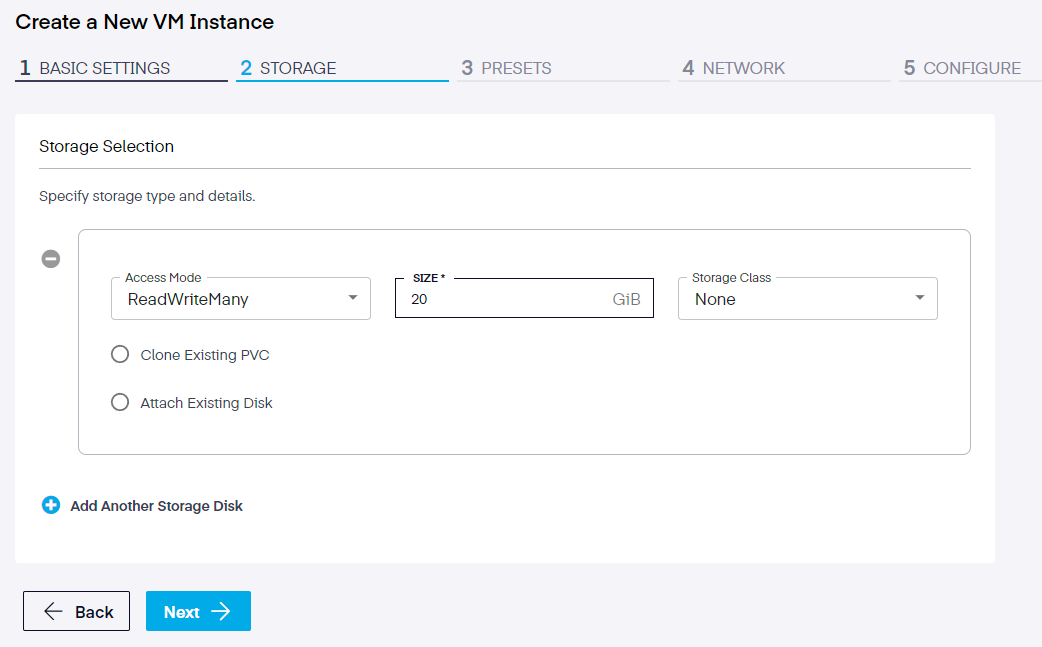
Step 2. Storage Selection
Here, users define the specific storage type and other details. The options are:
- ReadWriteMany or ReadWriteOnce
- The size in GiB
- Storage Class
User also have the option to Clone an Existing PVC or Attach an Existing Disk.
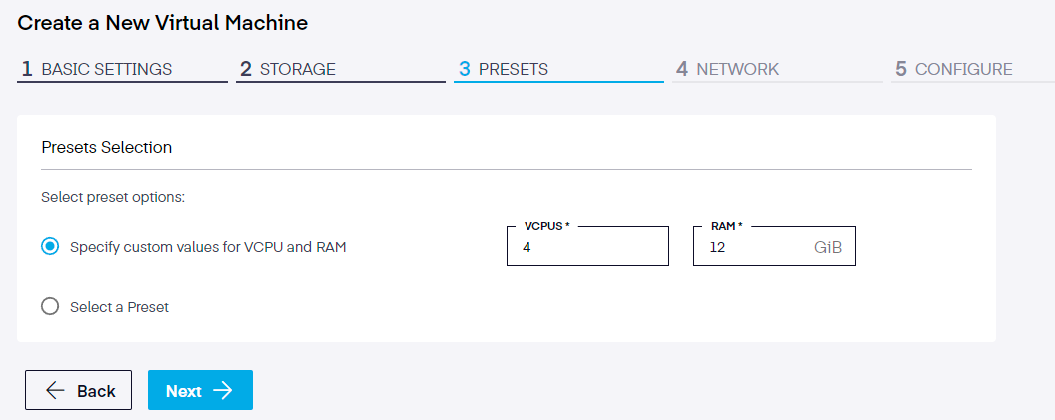
Step 3. Preset Selections
In this step, users select one of two options; either a preset value or manually define values for the number of VCPUs and amount of RAM.
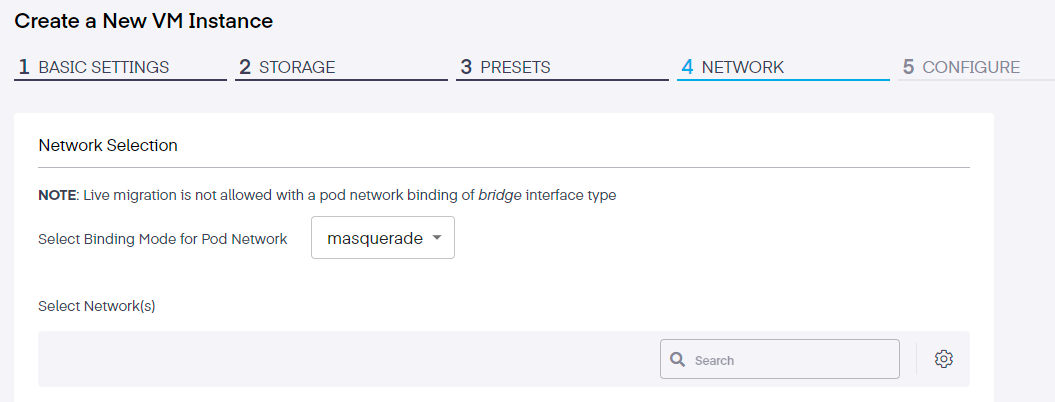
Step 4 Network Selection
You have two options when selecting the Binding Mode for Pod Network:
- Masquerade - In this mode, KubeVirt allocates internally NAT'd IP addresses to the image
- Bridge - Here, virtual machines are linked to the network backend via a linux "bridge"
Live migration is not allowed with a pod network binding of bridge interface type
Step 5. Configure Instance Details
Kubevirt utilizes cloud-init as a sort of templates, similar to a kubevirt VM or VMI yaml config. these can be a useful tool, especially when debugging test cases. Here, users can either enter a cloud-init script or upload a cloud-init file.
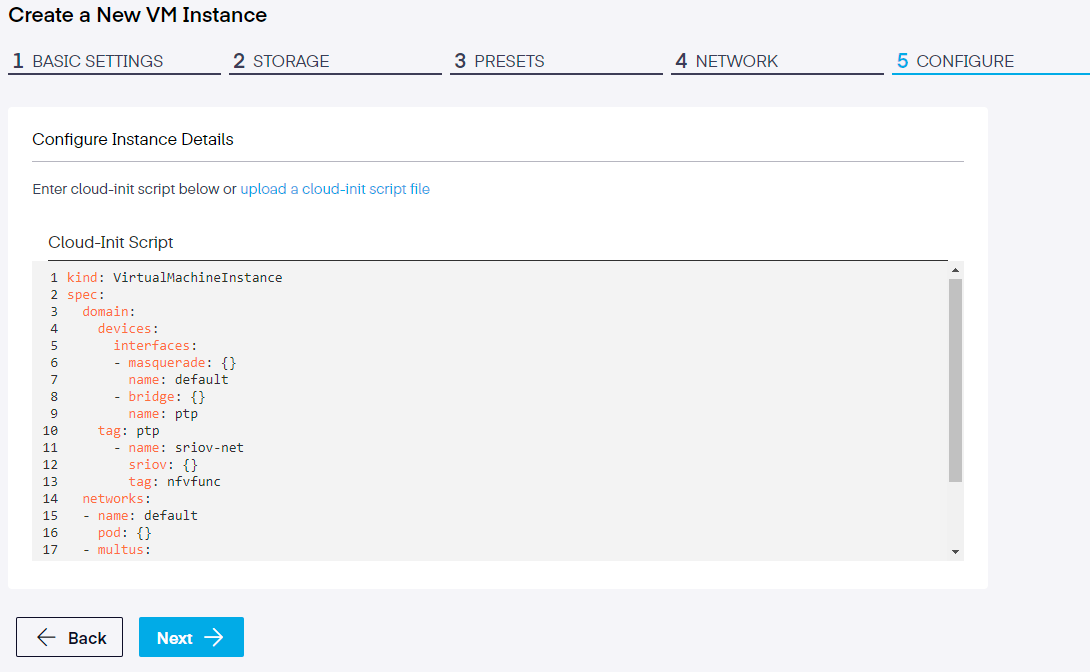
Step 6. Advanced Options
In this section, further details can be added via a YAML file. Below, we appended an additional dataVolume.
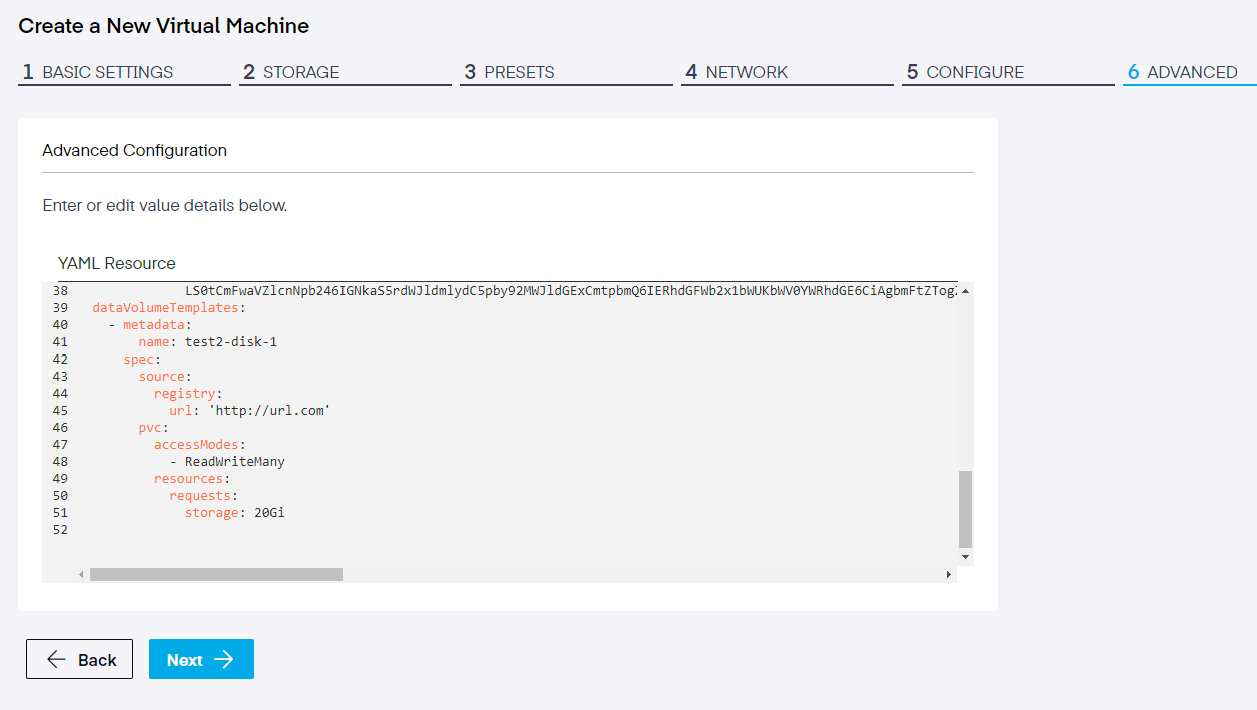
Step 7. Review and Create
In the final step, we analyze our choices to ensure they are correct. If a value needs to be corrected, we can still go back using the
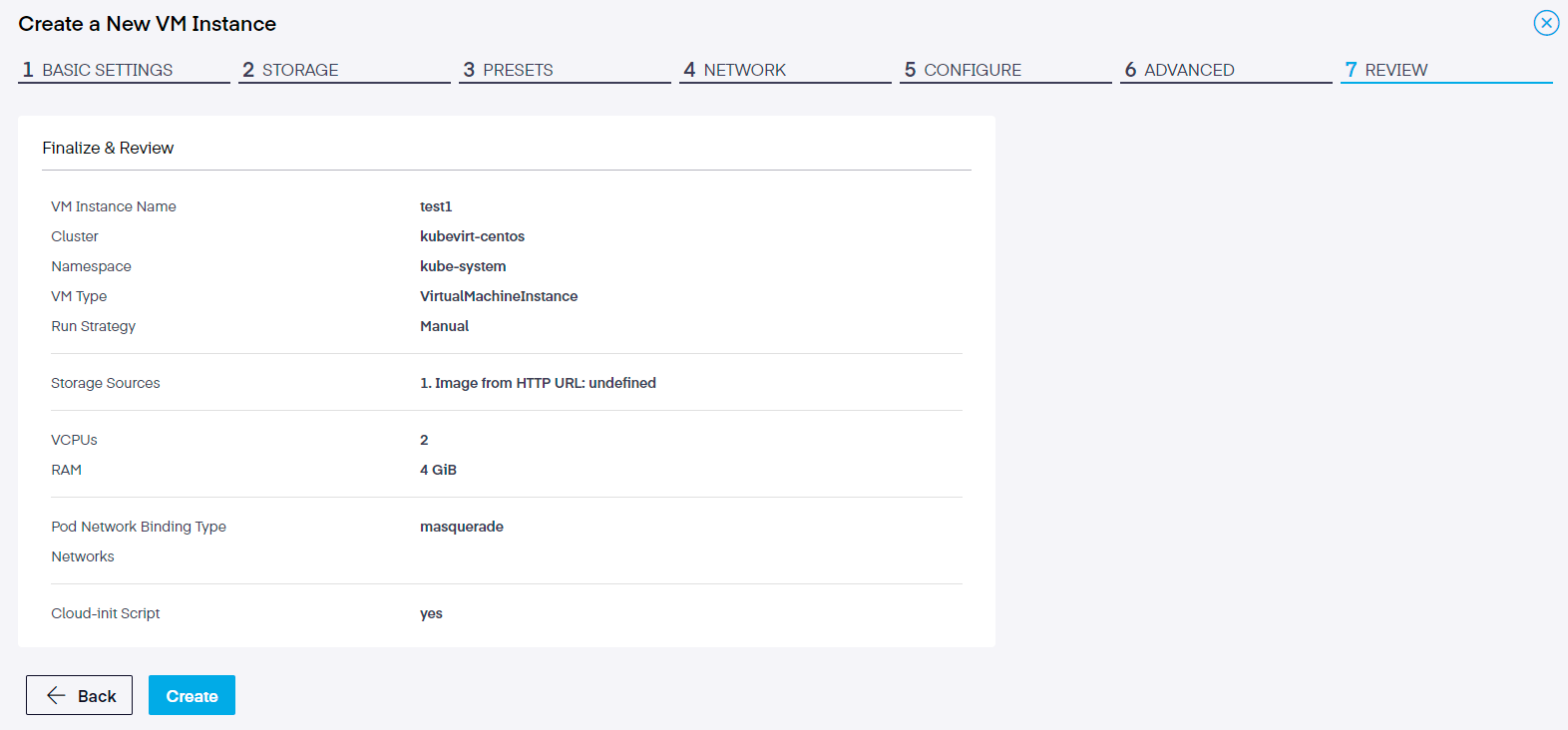
If satisfied with the settings, click the
Should you have thoughts, questions or issues with this process, please do not hesitate to reach out to our support team for more information.