Onboarding a PMK BareOS Cluster to Azure Arc
Introduction
In this tutorial, we will demonstrate how to connect an existing Platform9 Managed Kubernetes (PMK) cluster to Azure Arc using a service principal. A service principal is a unique and restricted management identity that is given only the minimum permission settings necessary to link machines to the Azure infrastructure.
What is Azure Arc?
Azure Arc is a new Microsoft product that simplifies the management of complex and distributed environments across on-premises, edge, and multi-cloud locations. The Azure Arc control plane enables developers to build hybrid and multi-cloud architectures for applications. Azure Arc expands the Azure management plane capabilities and resources to run on other clouds and on-premises. It also allows users to manage the following resource types hosted outside of Azure:
- Servers - both virtual and physical servers running both Windows or Linux.
- Kubernetes clusters - supports various Kubernetes distributions.
- Azure data services - Including Azure SQL Managed Instance and PostgreSQL Hyperscale services.
- SQL Server- - Users can enroll instances from any location with SQL Server on Azure Arc-enabled servers.
Prerequisites
- A Kubernetes cluster on Platform9 Managed Kubernetes (PMK). If you don't have it already, Signup for a Free PMK Account Here and create your Kubernetes cluster using PMK.
- A Kubectl installation with your Kubernetes cluster from the step above configured as the primary cluster.
- Azure account with Azure Arc services enabled, and the Azure CLI installed
Testing was done with kubectl 1.19.6, azure cli 2.27.0.
Step 1 - Prep your local environment
Use the following Azure command to add the connectedk8sand k8s-configuration extensions.
Step 2 - Create Azure service principal
In this step we create a new service principal (SP) with a descriptive name that is specific to your Azure Active Directory tenant. We also designate the role of the contributor to this user while passing the appropriate --scope__argument.
The output of the command should be similar to this:
Step 3 - Apply permissions
We can assign roles to the newly created service principal. The built-in Azure subscription role with limited permissions only allows the principal to register clusters to Azure. The principal with this assigned role cannot update, delete, or modify any other clusters or resources within the subscription. This feature also allows admins to restrict cluster registration to a resource group scope. The following scenarios are seen above:
- Subscription - scope /subscriptions/xxxxxx
- Resource Group - - scope /subscriptions/_xxxxxx/resourceGroups/myGroup_
The options are noted below.
Use the following parameters and values when applying these permissions:
Step 4 - Register service providers
Specifically register the resource providers for a subscription
Step 5 - Create a new Azure resource group
Create a resource group where the PMK cluster to be placed
The output of the command should be similar to this:
If an existing resource group is present, it can be used instead of creating a new one. Note the setting in the next step that mentions the |
Step 6 - Set Azure environment variables
To make things more readable (and easier) we assign all needed values to environment vars.
Step 7 - Login to Azure subscription using service principle
To login using the service principal, invoke the ServicePrincipalparameter of the Connect-AzAccount cmdlet. You will also need the service principal's application ID, sign-in credentials, and the tenant ID associate with the service principal.
Step 8 - Connect the PMK cluster to Azure Arc
Here, we connect the existing PMK cluster to Azure Arc. If the command lacks a defined location parameter, Arc creates the Kubernetes enabled resource in the same location as the resource group. To create an Arc enabled Kubernetes asset in a different location, specify either the --location <region> or the -l <region> when running the command below.
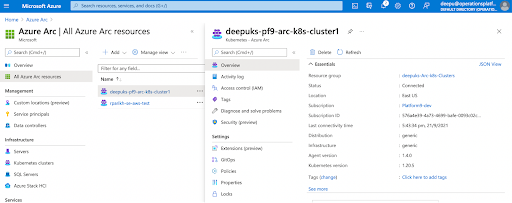
Validate Azure Arc integration
The cluster should now be visibly onboarded as part of a new Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes resource.
Using kubectl with a context of the PMK cluster, we can verify the integration by runningkubectl get pods -A from the command line. In the output, we should see the Azure Arc agents running in the cluster.