Calico CNI
This article describes Platform9 Managed Kubernetes (PMK) support for Calico as one of the supported CNI integrations.
What is Calico
Calico is a popular Layer 3 based networking solution that is used to interconnect virtual machines or Linux containers thanks to virtual routers. For more information on Calico, refer to Project Calico website.
Calico provides a Cluster Network Interface (CNI) plugin that can be used for integration with Kubernetes.
Platform9 Managed Kubernetes supports integration with Calico for pod-to-pod and external cluster communications.
When Calico is installed in a Kubernetes cluster, the key components of like calico-controller,calico-node and typharun as pods on the Kubernetes nodes. It should be noted that typha uses port 5473. See the related documentation for more info.
Calico uses iptables and route table to route traffic between Kubernetes nodes.
For a detailed introduction to Calico and Calico routing, please see an introduction here.
Prerequisites
Following are the requirements to keep in mind when creating Calico enabled clusters.
- Subnets on a network should not coincide. You cannot have two clusters with container CIDR or service CIDR being the same on one L2 domain or network.
- If your cluster nodes are Virtual Machines, and if you plan to use Calico with encapsulation disabled, then port security should be disabled for these VMs. This allows egress traffic from your pods using the IP assigned from the Container or Services CIDR pool.
Provider Support Matrix
Calico CNI is only supported on the following PMK providers today.
| Provider | Support for Calico | |
|---|---|---|
| BareOS Provider | Yes | |
| AWS Provider | Yes | |
| Azure Provider | No |
Configuring Calico
Calico supports multiple networking configuration options. You will see these options in the PMK Cluster creation wizard when you choose Calico as your preferred CNI for the cluster.
Following is a brief overview of them and what subset is supported by PMK.
Encapsulation
Calico supports two types of encapsulation: IP-in-IP and VXLAN. PMK supports Calico with IP-in-IP encapsulation mode only.
Ip-in-Ip is a simple form of encapsulation, achieved by putting an IP packet inside another. A transmitted packet contains an outer header with host source and destination IPs and an inner header with pod source and destination IPs.
Calico Ip-in-Ip encapsulation supports the following configuration options:
- Always: Encapsulates POD traffic in IP-in-IP between nodes.
- CrossSubnet: Encapsulation when nodes span subnets and cross routers that may drop native pod traffic. This is not required between nodes with L2 connectivity.
- Never: Disables IP in IP Encapsulation. Sends packets as if they came directly from the pod. Since there is no encapsulation and de-encapsulation overhead, this mode is highly performant. When selecting this option, NAT Outgoing will be disabled.
See more details about these options here: https://docs.projectcalico.org/v3.11/networking/vxlan-ipip
NAT Outgoing
When NAT Outgoing is enabled, packets destined outside the pod network will be SNAT'd using the node's IP address.
Block Size
Block size determines how many pods can run per node vs total number of nodes per cluster.
For example, a block size of 22 enables 1024 IPs per node, and a maximum of 64 nodes per cluster.
Block size must be greater than 20 and less than 32 and not conflict with the Contain CIDR
MTU
This is the Maximum Transmission Unit size for the node's interface, specified in bytes.
Interface Detection Method
Interface detection method controls which ethernet adapter Calico will bind with for ingress/egress from the Kubernetes node.
There are multiple configurations:
First Found – The first-found option enumerates all interface IP addresses and returns the first valid IP address
Can Reach – The can-reach method uses your local routing to determine which IP address will be used to reach the supplied destination. Both IP addresses and domain names may be used.
IP_AUTODETECTION_METHOD=can-reach=8.8.8.8IP6_AUTODETECTION_METHOD=can-reach=2001:4860:4860::8888IP_AUTODETECTION_METHOD=can-reach=www.google.comIP6_AUTODETECTION_METHOD=can-reach=www.google.comInterface – The interface method uses the supplied interface regular expression (Golang syntax) to enumerate matching interfaces and to return the first IP address on the first matching interface.
IP_AUTODETECTION_METHOD=interface=eth.*IP6_AUTODETECTION_METHOD=interface=eth.*Skip Interface – The skip-interface method uses the supplied interface regular expression (Golang syntax) to exclude interfaces and to return the first IP address on the first interface that not matching.
IP_AUTODETECTION_METHOD=skip-interface=enp6s0f0,eth.*IP6_AUTODETECTION_METHOD=skip-interface=enp6s0f0,eth.*To learn more about Calico and Interface detection, please read the Calico documentation found here.
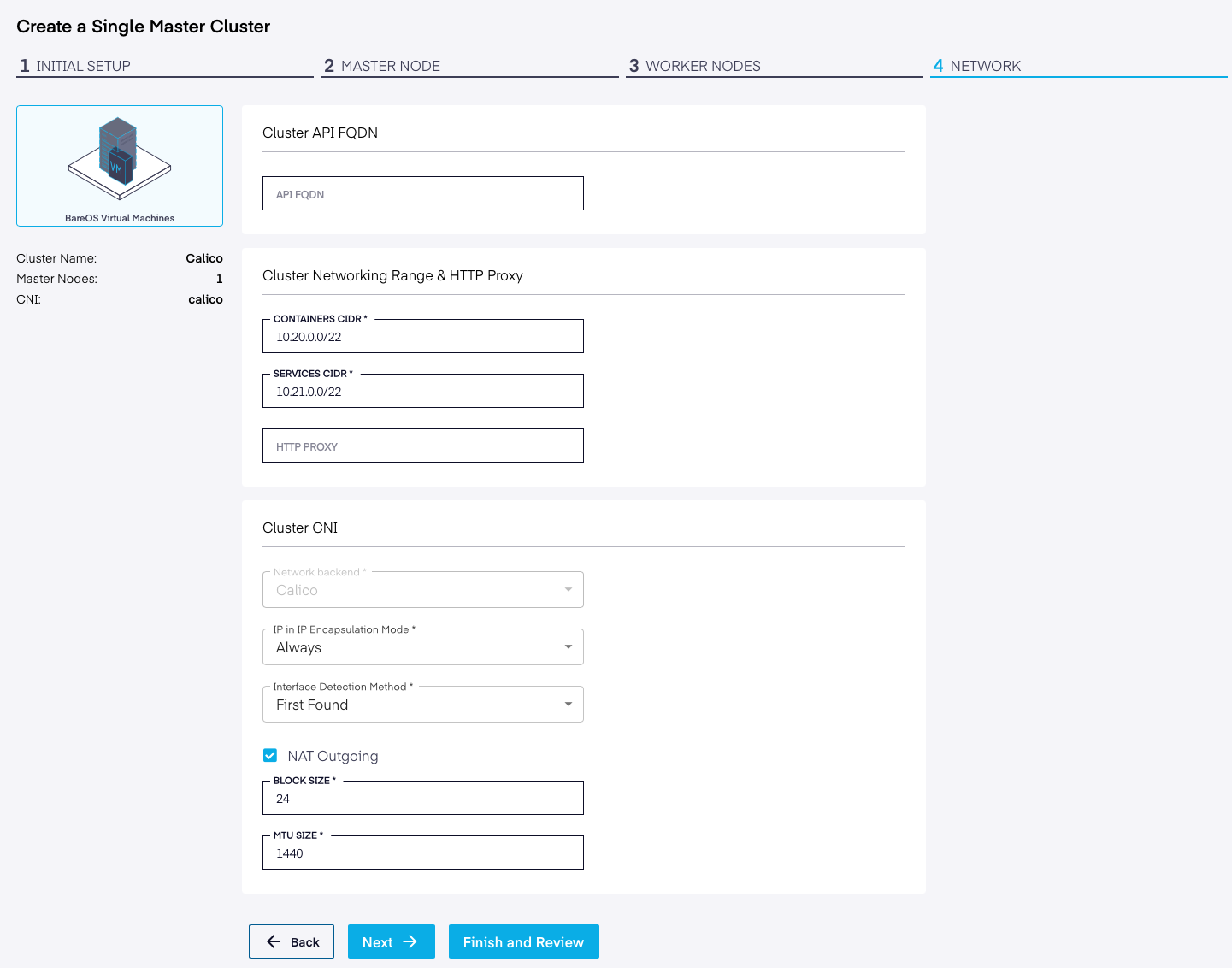
Create a Calico-enabled Cluster
While creating a new Kubernetes cluster using the PMK UI, in the wizard under Network Configuration, select Calico as the network backend.
Configure Network Policies
Once Calico has been installed, you can create network policies within Kubernetes for incoming and outgoing network traffic by editing the NetworkPolicy Kubernetes Resource.
Following is an example of a NetworkPolicy file.
For a full introduction and tutorials, please see Calico Security Policies.
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1kind: NetworkPolicymetadata: name: test-network-policy namespace: defaultspec: podSelector: matchLabels: role: db policyTypes: - Ingress - Egress ingress: - from: - ipBlock: cidr: 172.17.0.0/16 except: - 172.17.1.0/24 - namespaceSelector: matchLabels: project: myproject - podSelector: matchLabels: role: frontend ports: - protocol: TCP port: 6379 egress: - to: - ipBlock: cidr: 10.0.0.0/24 ports: - protocol: TCP port: 5978