Profile Engine Setup Guide
What is RBAC?
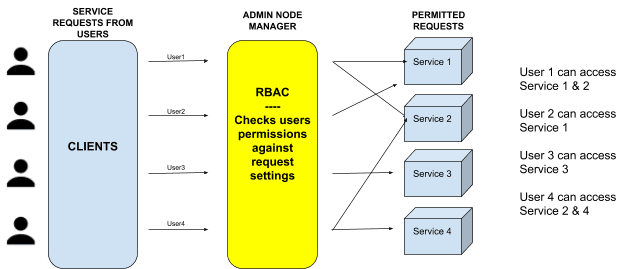
The Role-Based Access Control or (RBAC) system is composed of users, roles, and permissions and. It creates objects that allow validated users or groups access to objects and resources within a cluster. RBAC also defines what type of actions are permitted, grounded on the security principle of least privilege based on the user's role and function within the organization.
What is the RBAC Profile Engine?
The Platform9 RBAC Profile Engine is a new service which allows users to create, edit, deploy, and archive profile templates within their SaaS management plane. It enables a user to create a ‘snapshot’ of a known state, then set that snapshot as the main profile of that state. It can also save the profile, which can be used later as a template for new or existing clusters. In addition, the Profile Engine handles the Profile Lifecycle, Deployment, Enforcement, and Drift Analytics.
What is an RBAC Profile?
An RBAC Profile is a collection of Roles, ClusterRoles, RoleBindings, and ClusterRoleBindings stored on the Platform9 SaaS Management Plane. These objects act as a form of 'template' for cluster permissions managed by Platform9. The RBAC Profiles are produced from existing clusters, which can then be customized and deployed to any attached Platform9 cluster. The deployment process updates the target cluster's RBAC policies to ensure it conforms to the profile. Any policies that are external to the profile will be left unchanged.
Profile deployment is non-destructive. Platform9 does not remove Policies or API access from a cluster.
New profiles are created in a Draft state and cannot be deployed to clusters. Once a Profile is in a ready state, users can transition it from a draft form to a published state, which users can then deploy. An optional state is archived profiles. These cannot be deployed and are in a read-only state.
Cluster Creation with Profile Agent
Prerequisites
- SaaS Management Plane running PKM Version 5.3.1 (Next Gen Platform Only)
- A cluster running Kubernetes 1.20 (or a cluster running Kubernetes 1.20 with a previously deployed Profile Agent)
Create a New Profile
(Optional) If no clusters are running with the Profile Agent, you will need to create a new cluster and add the Profile Agent at the time of cluster creation. Using the advanced cluster wizard to select Kubernetes version 1.20, the Profile engine option will immediately become visible under the Application & Container Settings. Check the box next to that option to enable that feature. ** **
Step 1. Go to the Cluster Profiles tab, then click on Add RBAC Profile
Step 2. Select a cluster that the RBAC policies will be collected from and name it. This enables you to use the cluster as a default baseline for the new profile.
Step 3. Now select the Roles to add to the profile. Once selections are completed, click Next.
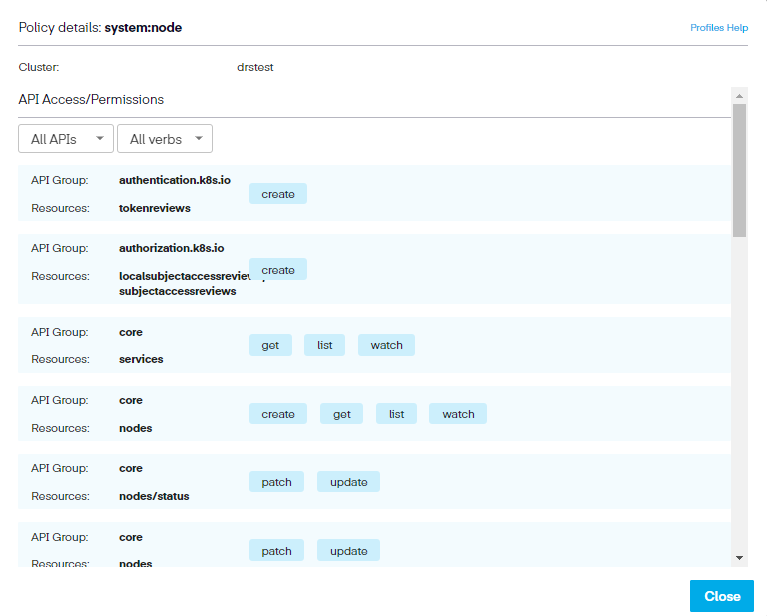
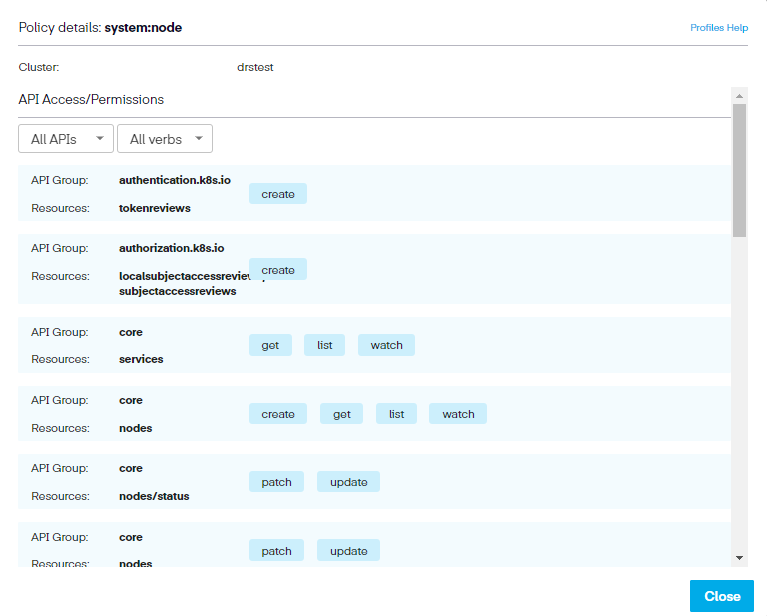
Next to each option, a small magnifying glass link opens the policy details that point out the permission settings available to that ClusterRole.
Step 4. In the ClusterRoles section, we repeat the process of selecting the needed ClusterRoles. Again, there are a significant number of options available (74 in total). To view the entire list, click the Rows per page dropdown menu and select 100.
Step 5. We can now begin choosing the RoleBindings. Identify the settings you want to allow and then click Next.
Step 6. Now we move onto ClusterRoleBindings. Select the settings you want to allow and then choose Next.
Step 7. This opens the Review page, where we can assess our choices before completing the profile. In the review section, we have asked the profile engine to connect to this cluster and use the settings for these Roles, ClusterRoles, RoleBindings, and ClusterRoleBindings. The profile engine then contacts the agent running in the cluster and tells it to create the profile. Once completed, it moves to a ‘Draft' status. This simply means that the profile has been generated but cannot be used yet. Since the UI polls every 30 seconds to check for updates, the changes happen quickly.
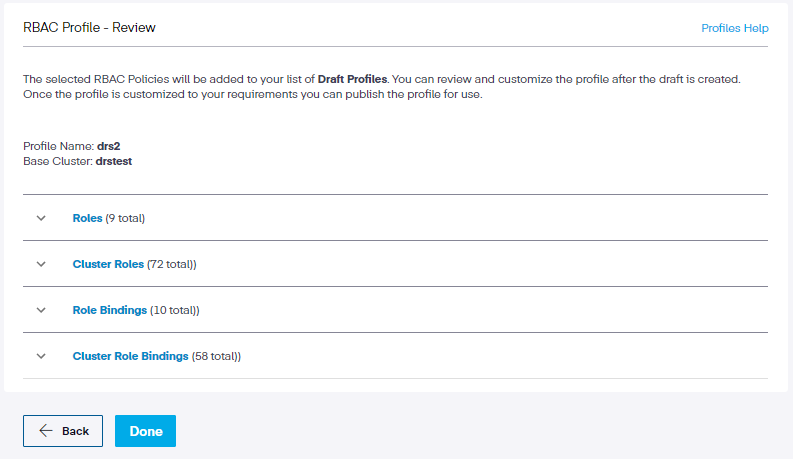
Under each policy, we can click the dropdown to review the choices we have made.
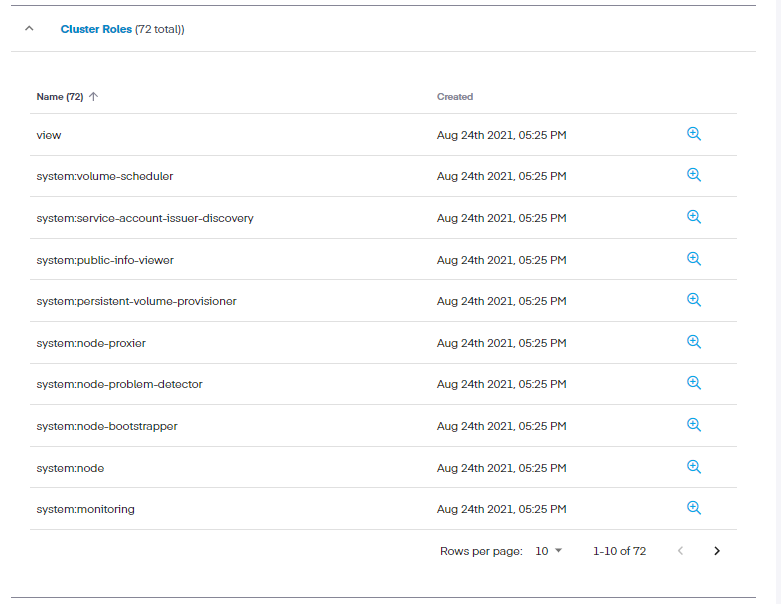
Permission information can be reappraised by clicking the magnifying glass icon link across from each setting. Also, we can sort the permissions based on API access or Verbs, which show only those resources authorized for that action.
Step 8. Lastly, click Done. This saves the profile and adds it to our list of profiles as a draft. We can then publish the profile and then deploy it.
Edit Profile
If we need to modify a profile, we can select it using the radio button and then use one of the three icons above the profile name, which becomes available to use. The three options are as follows.
- Manage Bindings
- Edit
- Delete
Using the edit function, we can return to the menu and choose one of the four tabs (Roles, ClusterRoles, RoleBindings, and ClusterRoleBindings). We then modify its settings in the RBAC Profile, where we can also see the available namespaces.
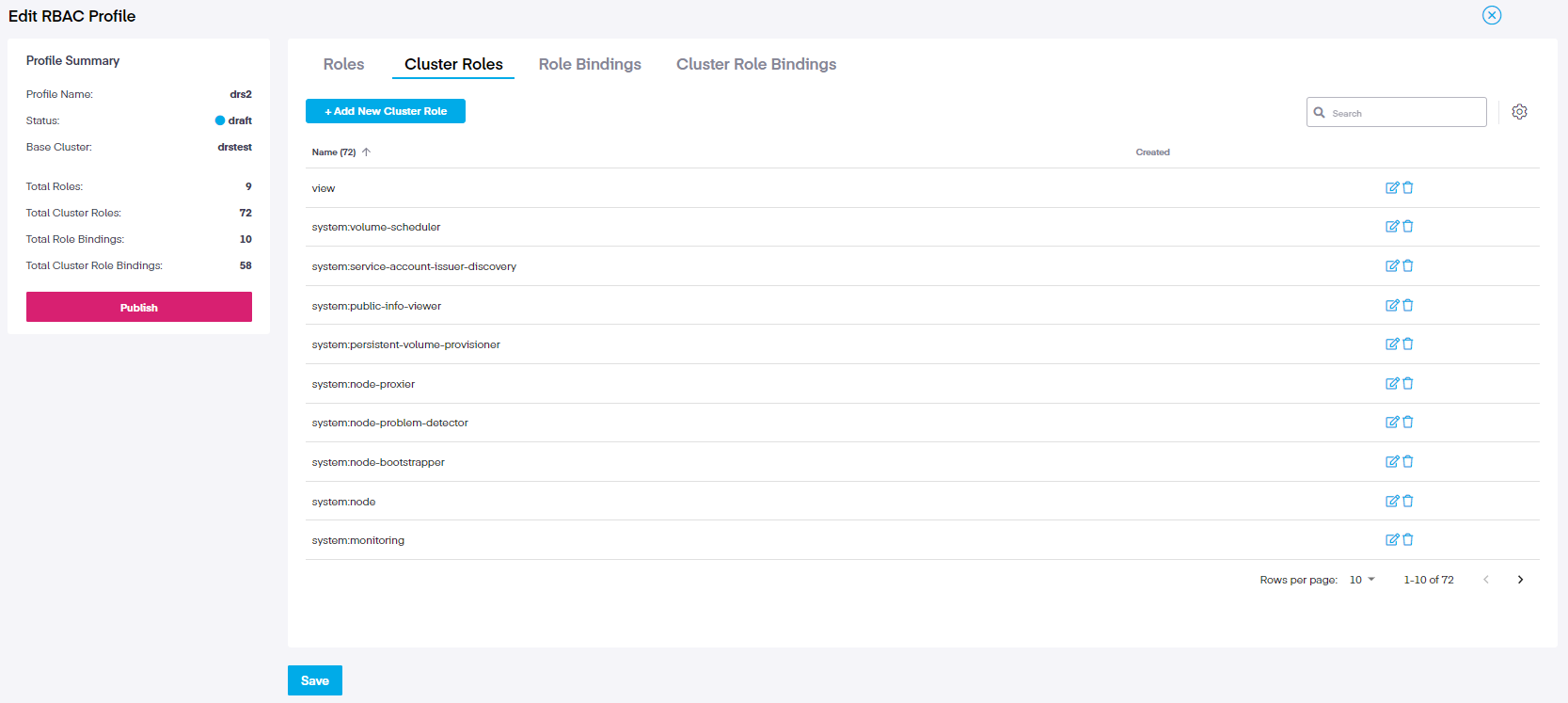
For example, if we choose the ClusterRole tab and the click on the small edit icon to the right of each role, it opens a new window which allows further editing of the resources, which will search the linked cluster and show any additional verbs that may not be included in the policy.
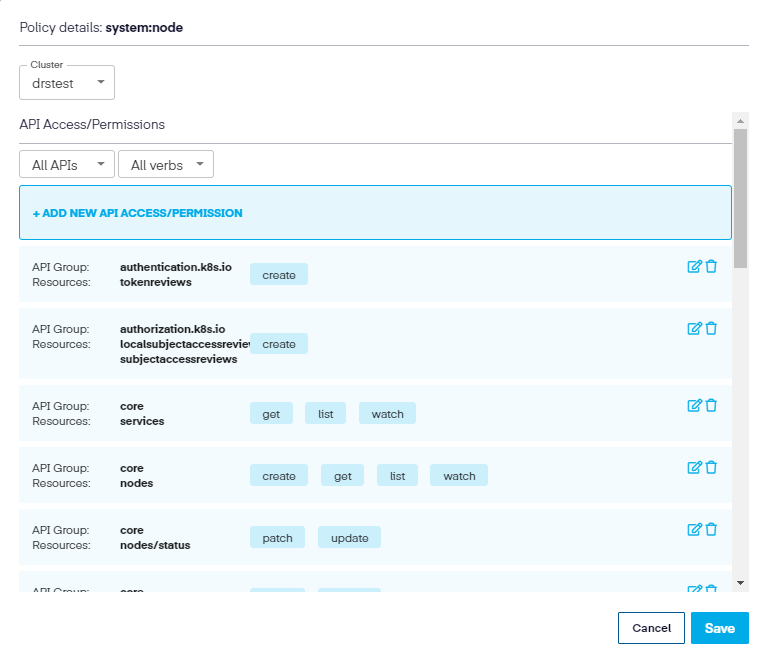
We can then modify the resource further by clicking the Edit icon to the right and add any auxiliary verbs needed to the resource.
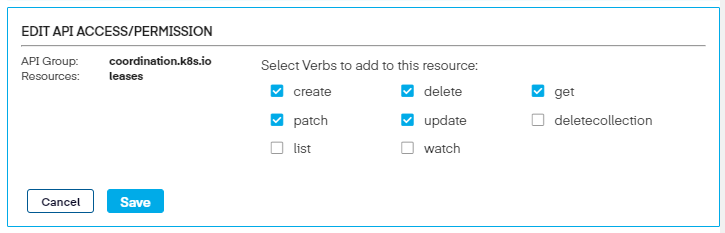
Lastly, click Save three times to updates the policy, and brings us back to the edit screen.
Add Roles
In the Edit RBAC Profile screen, we can also add additional Roles, ClusterRoles, RoleBindings, and ClusterRoleBindings to existing profiles. To accomplish this, select the tab to choose the role to update and then click on (in this example) the Add New Cluster Role.
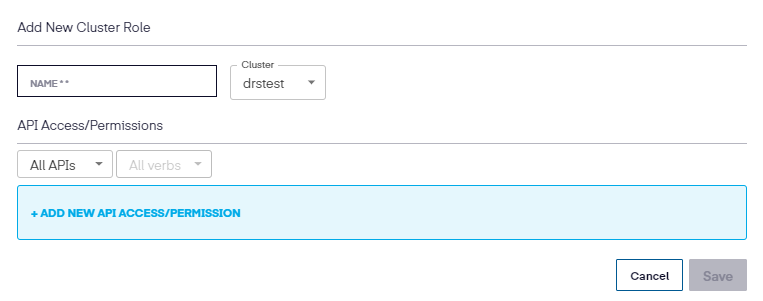
Next, add the name, select the cluster, and then the new API Access/Permission.
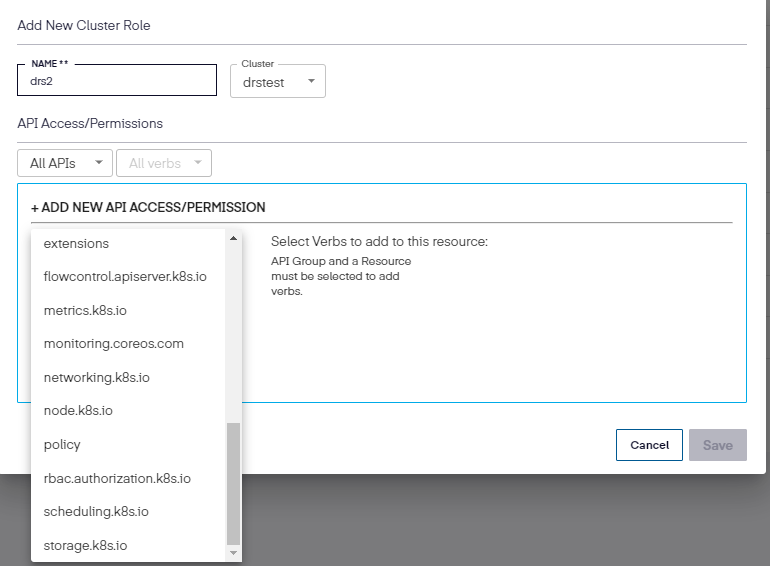
Once the API Group and resource is chosen, select the permissions to be used.
Once completed, click Add, then Save to update the New Cluster Role.
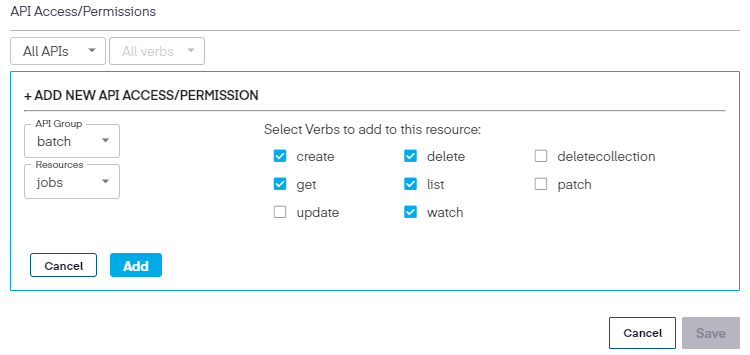
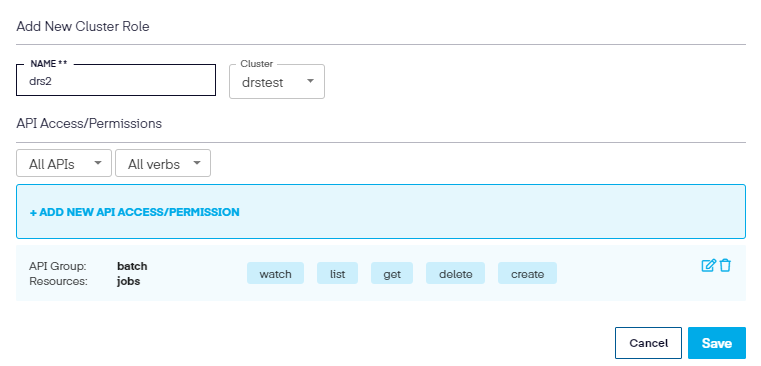
When returned to the edit screen, click Save again to complete the modification.
To add an RBAC Policy without an existing cluster use the YAML view of the Add Role, Cluster Role or Role Bindings of Cluster Role Bindings
Permission Types Quick View
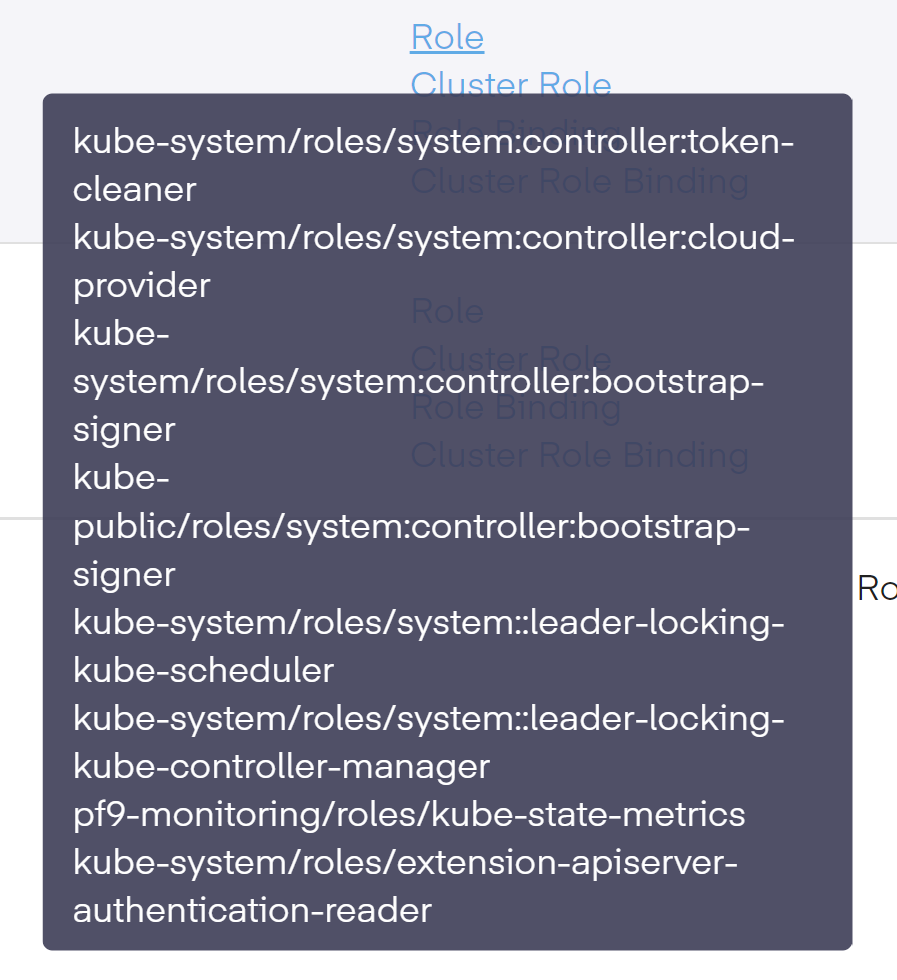
As an additional element, once back in the main RBAC Profile screen, we can review the different permissions for the Roles, ClusterRoles, RoleBindings, and ClusterRoleBindings types by momentarily hovering our mouse over each role.

This shows us the currently assigned permissions of each role.