External Cluster Operator
What is ECO?
The External Cluster Operator (ECO) is a component for securley managing EKS, AKS and GKE clusters. ECO is installed into EKS, AKS or GKE clusters after they have been imported to Platform9, and creates an outbound tunnel that securely connects the cluster to the Platform9 SaaS Management Plane. By leveraging ECO, all clusters, whether they operate with a public or private API Server, can be managed by Platform9.
Without ECO Platform9 is unable to communicate with the clusters API server which will prevent the Workloads, App Catalog, Monitoring and RBAC dashboards from functioning.
Benefits of Using ECO
Once connected, ECO, enables users to leverage Platform9 Managed Add-ons, such as in-cluster monitoring, deploy apps using the Helm Service and quickly troubleshoot applications running in the cluster by using the Workloads dashboards.
Zero-Setup GitOps Using ArgoCD
ECO also enables EKS, AKS and GKE clusters to be automatically added to ArgoCD with zero setup. Once ECO has established the secure communications tunnel to Platform9, the cluster is added to ArgoCD and users can immediately begin deploying applications or applying Kubernetes policies that are stored in their Git Repositories.
Installing ECO
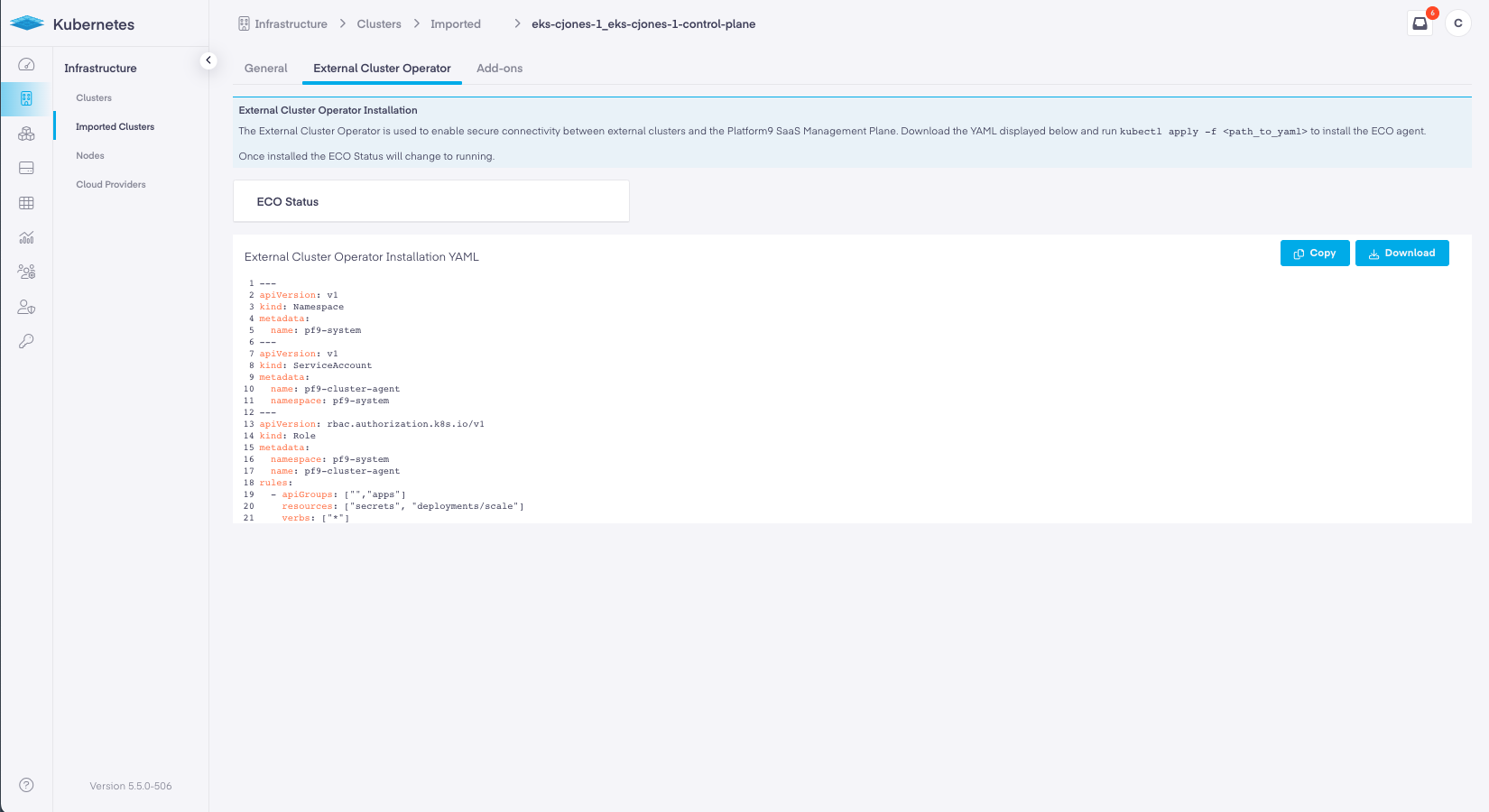
The External Cluster Operator is installed after importing a cluster, it is a discrete and separate step as the External Cluster Agent that ECO installs requires a secure endpoint that the cluster import process configures. After importing the external cluster a per-cluster specific ECO configuration is generated and provided as YAML that is applied using Kubectl to the external cluster.
Step 1 Import the external cluster
Follow the steps for importing an EKS, AKS, or GKE cluster, once the cluster is imported the ECO YAML can be accessed.
Step 2 Install ECO YAML
After importing the cluster, install ECO by utilizing one of the following three methods.
- Click on the Install ECO link in the Imported Clusters table,
- OR, Select the cluster using the radio button and click 'Edit' in the table action bar, then navigate to the External Cluster Operator tab.
The External Cluster Operator tab on the Edit Cluster dashboard provide the YAML required to install ECO into the imported cluster.
The YAML generated to install ECO is unique to each imported cluster and cannot be used in any other external cluster.
On the ECO tab, copy or download the YAML and save it to a location where the Kubectl client can access it.
Using Kubectl and the kubeconfig for the matching imported cluster run the following command:
kubectl apply -f <fileLocation>/<fileName>Once ECO is installed and running the status of ECO will updated to connected.
Understanding ECO Health Status
ECO is critical to connecting and managing external clusters, if ECO is not installed, or has failed Platform9 will be unable to communicate with the cluster's API server. When Platform9 is unable to communicate with the API server the following service will be unavailable:
- All Workloads Dashboards
- All Storage Dashboards
- All Monitoring Dashboards
- All RBAC Dashboards
- All ArgoCD Features
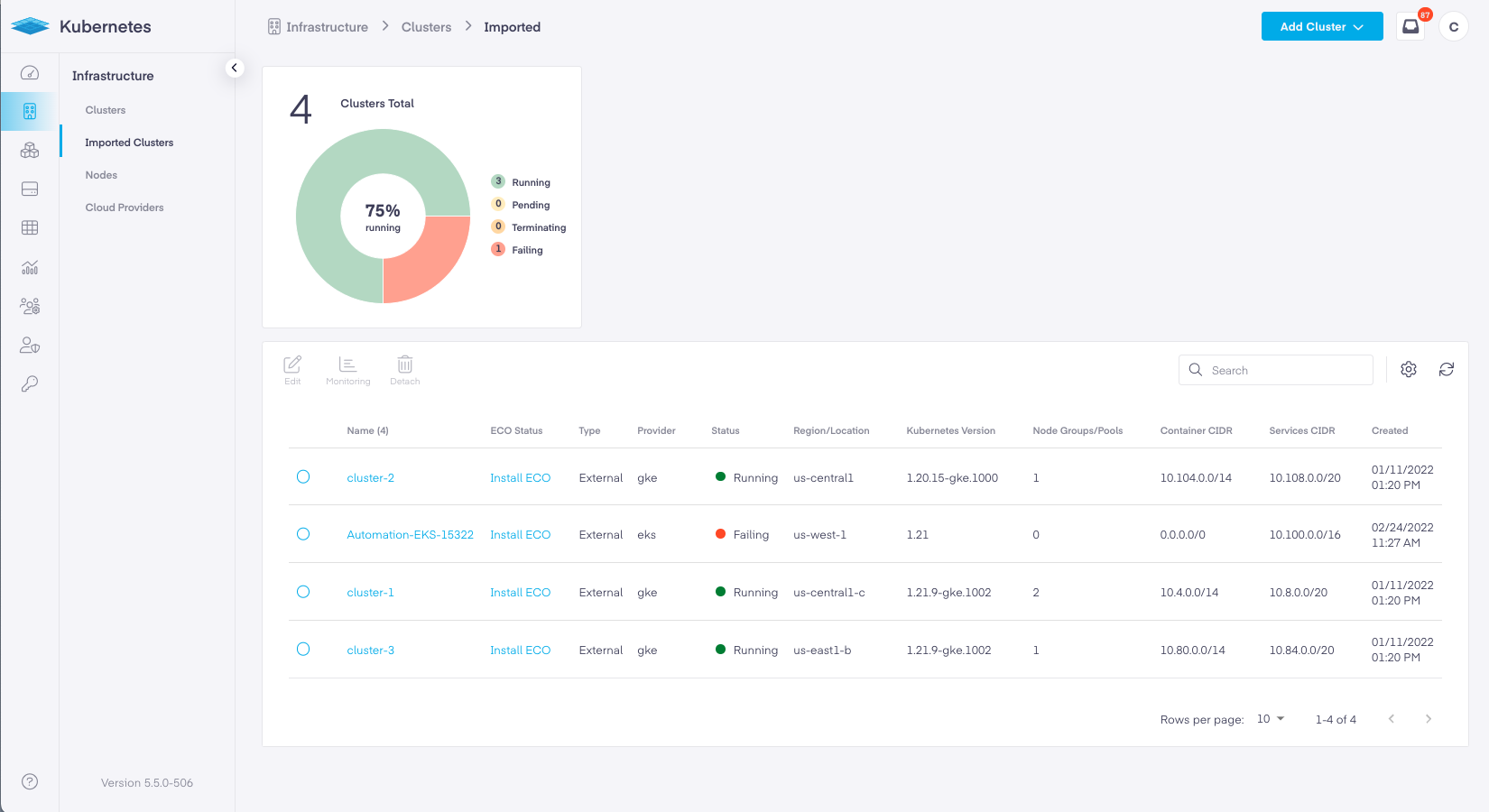
To view the status of ECO for any imported cluster navigate to Infrastructure -> Imported Clusters.
The Imported Clusters dashboard shows all imported clusters, the cloud they operate within, their health status as returned from the cloud they operate within, and the status of ECO. If ECO is not installed or is failing it will be displayed in red in the second column.
ECO Status can also be viewed for each individual cluster by selecting the radio button within the Imported Clusters Table and clicking Edit in the table action bar.
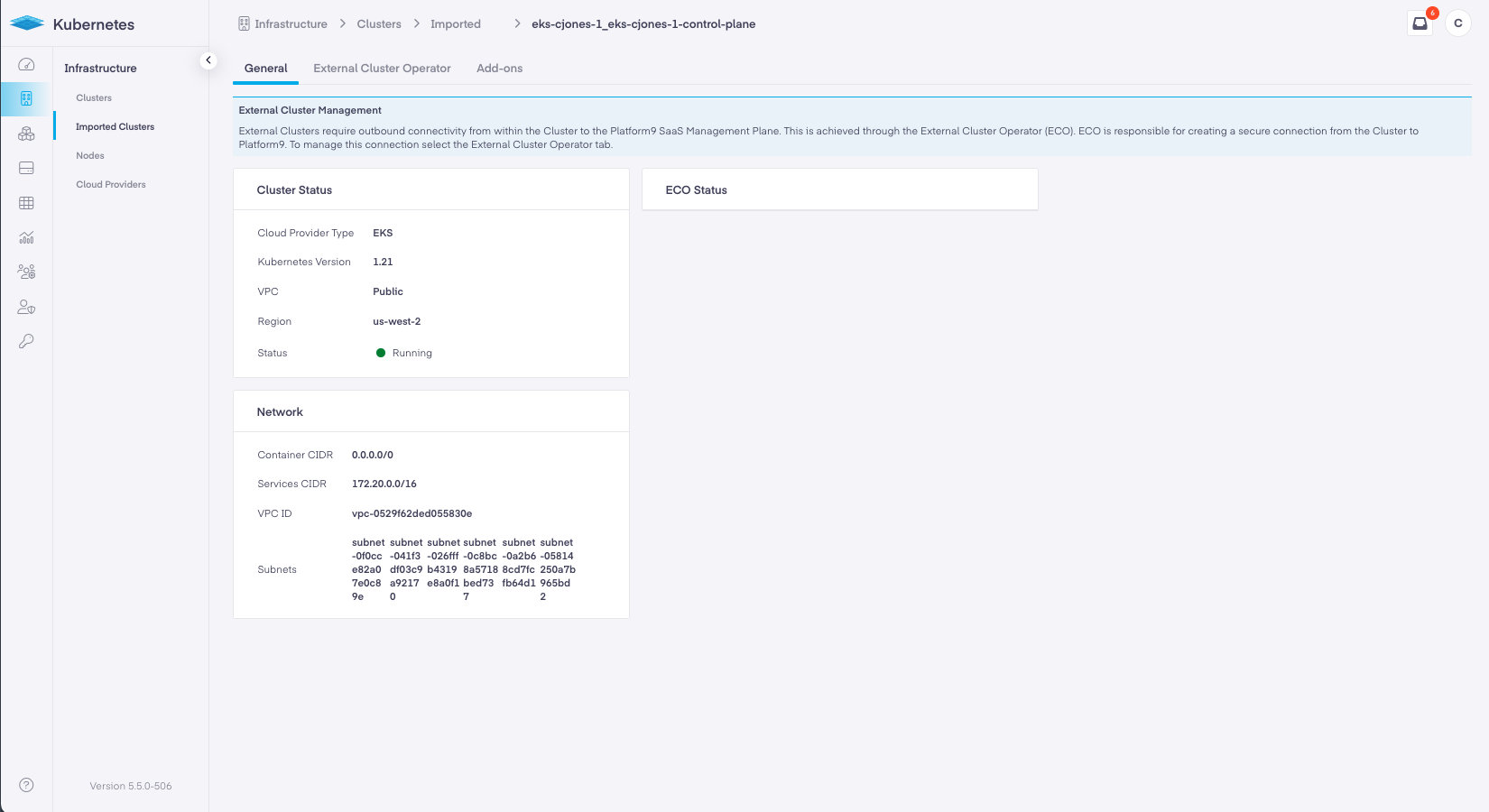
Both Edit Cluster General tab and the External Cluster Operator tab display the status of ECO.
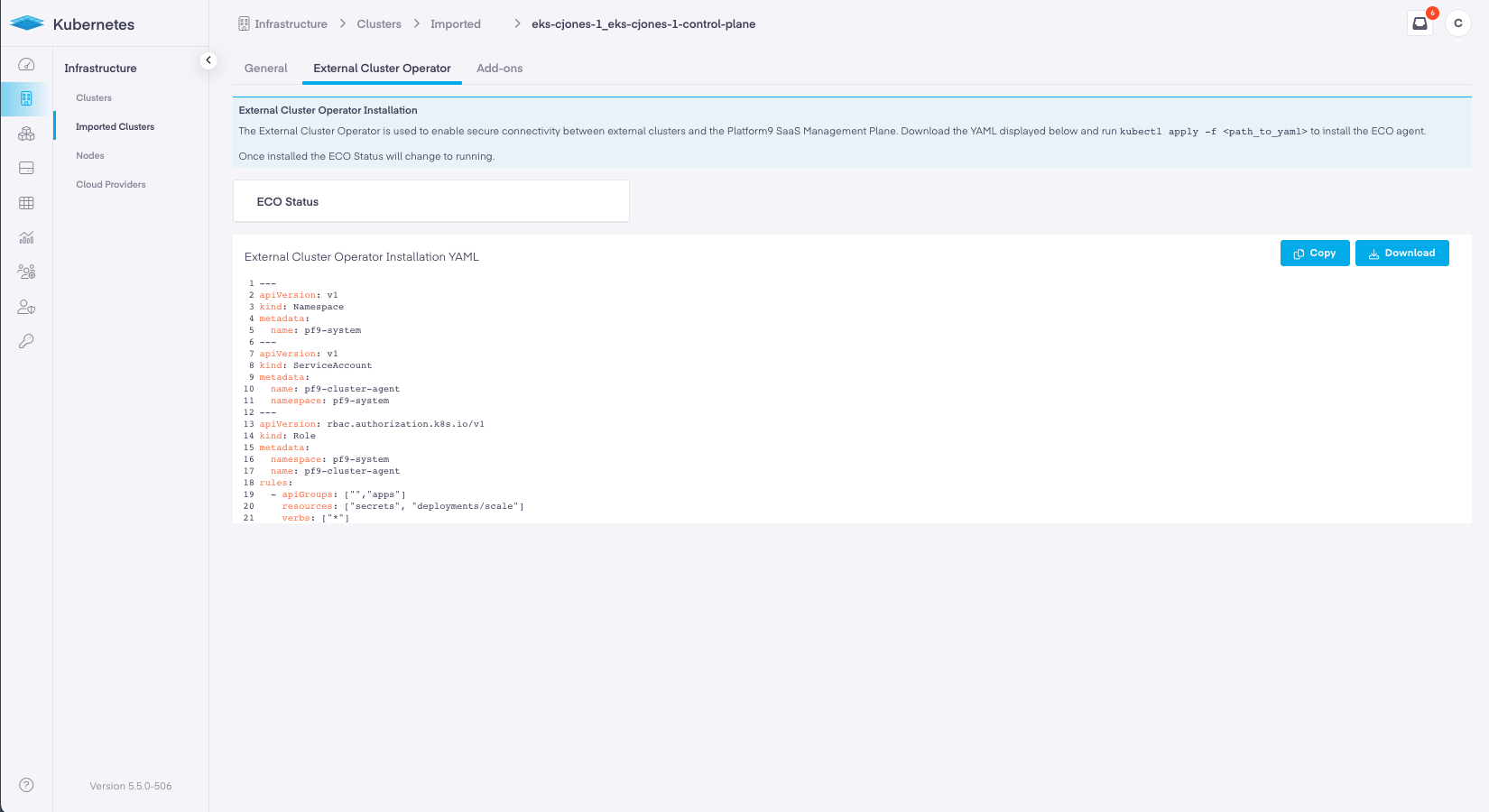
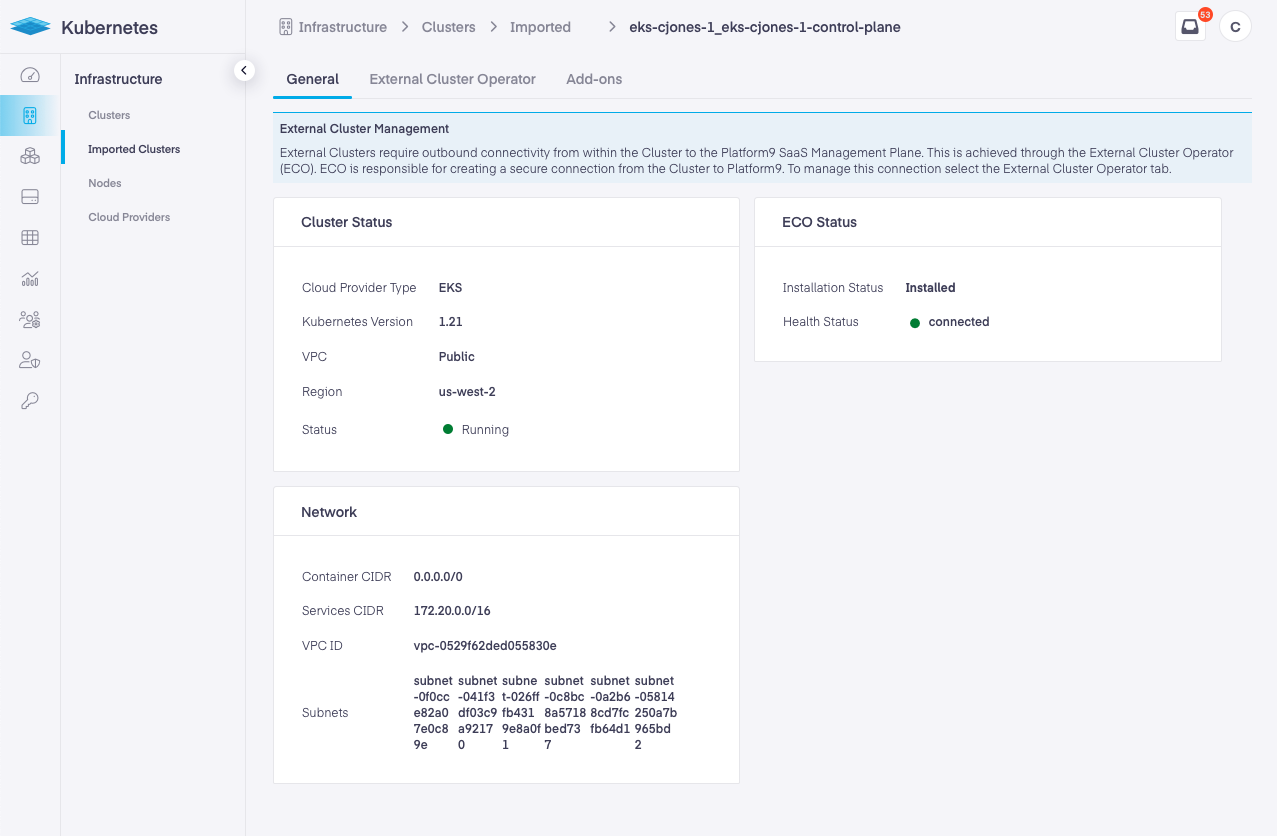
Imported Clusters with ECO Running
Below is the view a user would see with ECO actively running.
Removing ECO
Since the agent that is deployed on the cluster utilizes its own namespace, deleting the namespace will remove the agent.